As you age, it's important to prioritize your health and well-being. A plant-based diet can be a powerful tool for improving your overall health, especially if you're looking to reduce your risk of chronic diseases, manage your weight, and increase your energy levels.
In this guide, we'll explore the benefits of a plant-based diet for older women, provide tips for getting started, and offer delicious plant-based recipe ideas.
Table of Contents
What is the difference between a Plant-based diet, vegan diet and vegetarian diet
While these terms are often used interchangeably, there are distinct differences between them.
Plant-Based Diet
- Definition: A diet that primarily focuses on plant-based foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
- Key Characteristics:
- Can include varying levels of animal products, such as eggs, dairy, or honey.
- The emphasis is on reducing animal product consumption.
- Flexibility allows for personal preferences and dietary needs.
Vegan Diet
- Definition: A strict plant-based diet that excludes all animal products, including meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, and honey.
- Key Characteristics:
- Adheres to ethical and environmental concerns related to animal agriculture.
- Requires careful planning to ensure adequate nutrient intake.
- Often includes plant-based alternatives for animal products.
Vegetarian Diet
- Definition: A diet that excludes meat, poultry, and fish.
- Key Characteristics:
- Can include varying levels of animal products, such as eggs and dairy.
- Often focuses on ethical or health concerns related to meat consumption.
- Provides flexibility in terms of dietary choices.
In summary:
- Plant-based diets offer a broad range of options, allowing for varying levels of animal product consumption.
- Vegan diets are strictly plant-based, excluding all animal products.
- Vegetarian diets primarily exclude meat, poultry, and fish, but may include other animal products.
The choice between these diets often depends on personal preferences, ethical beliefs, health concerns, and cultural factors.
Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet
A plant-based diet is one that primarily focuses on plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. While there are different variations of plant-based diets, such as vegan and vegetarian, the common thread is a reduced consumption of animal products like meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy.
Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet for Older Women:
- Improved heart health: A plant-based diet is rich in fiber, antioxidants, and healthy fats, which can help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Weight management: Plant-based foods are generally low in calories and high in fiber, making them a great choice for weight management.
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases: Studies have shown that a plant-based diet can reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes, certain types of cancer, and other chronic diseases.
- Increased energy levels: The nutrients in plant-based foods can help boost energy levels and reduce fatigue.
- Better digestion: Plant-based foods are often high in fiber, which can help improve digestion and prevent constipation.
Getting Started with a Plant-Based Diet
If you're new to plant-based eating, it's important to start slowly and make gradual changes to your diet. Here are some tips to help you get started:
- Focus on incorporating more plant-based foods: Start by adding more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds to your meals.
- Reduce your consumption of animal products: Gradually decrease your intake of meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy.
- Find plant-based alternatives: There are many plant-based alternatives available for common animal products, such as plant-based milk, yogurt, cheese, and meat substitutes.
- Don't be afraid to experiment: Try new plant-based foods and recipes to find what you enjoy.
Key Nutrients to Focus On
When transitioning to a plant-based diet, it's important to ensure you're getting enough of certain essential nutrients. These include:
- Protein: Legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds are all excellent sources of protein.
- Iron: Leafy greens, legumes, whole grains, and fortified foods are good sources of iron.
- Calcium: Leafy greens, legumes, fortified foods, and nutritional yeast are good sources of calcium.
- Vitamin B12: Fortified foods and nutritional yeast are good sources of vitamin B12.
Plant-Based Protein Sources
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, beans
- Whole grains: Quinoa, brown rice, oats
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds
- Tofu and tempeh
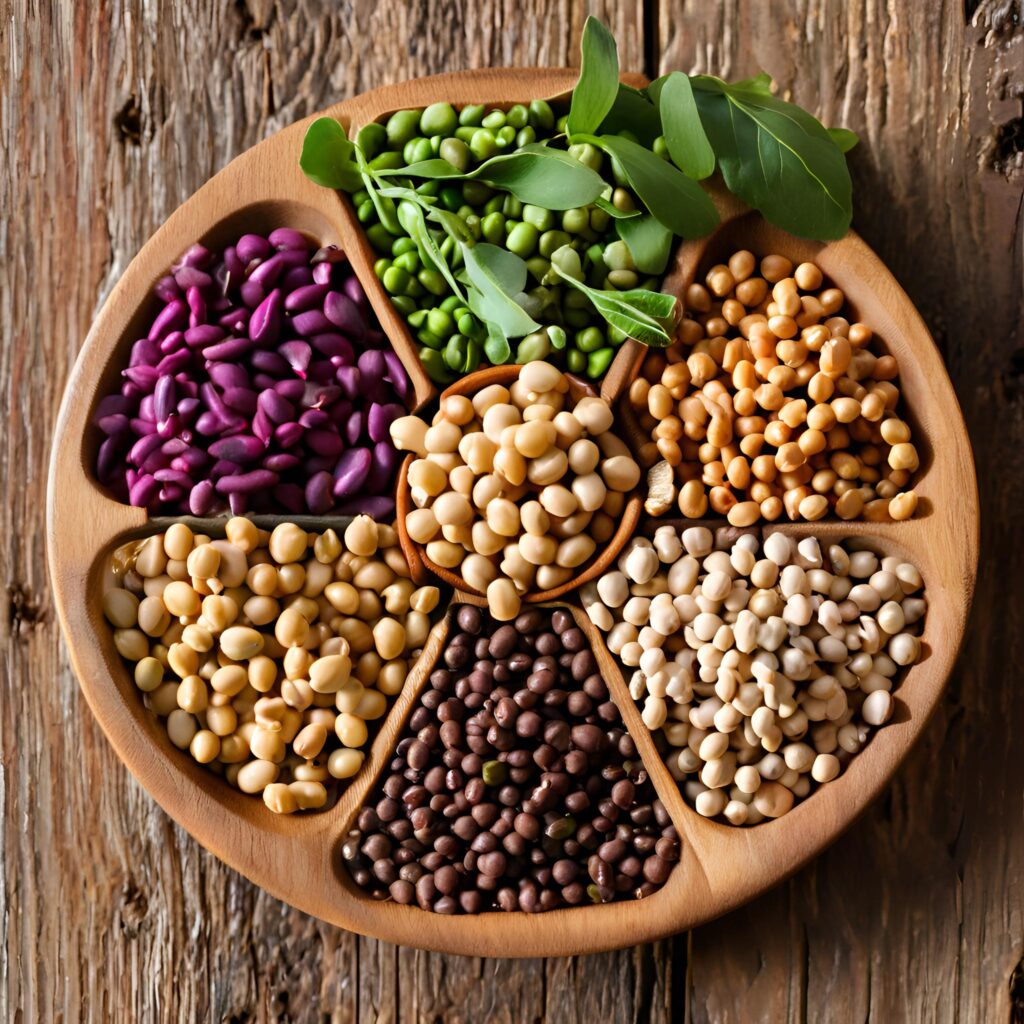
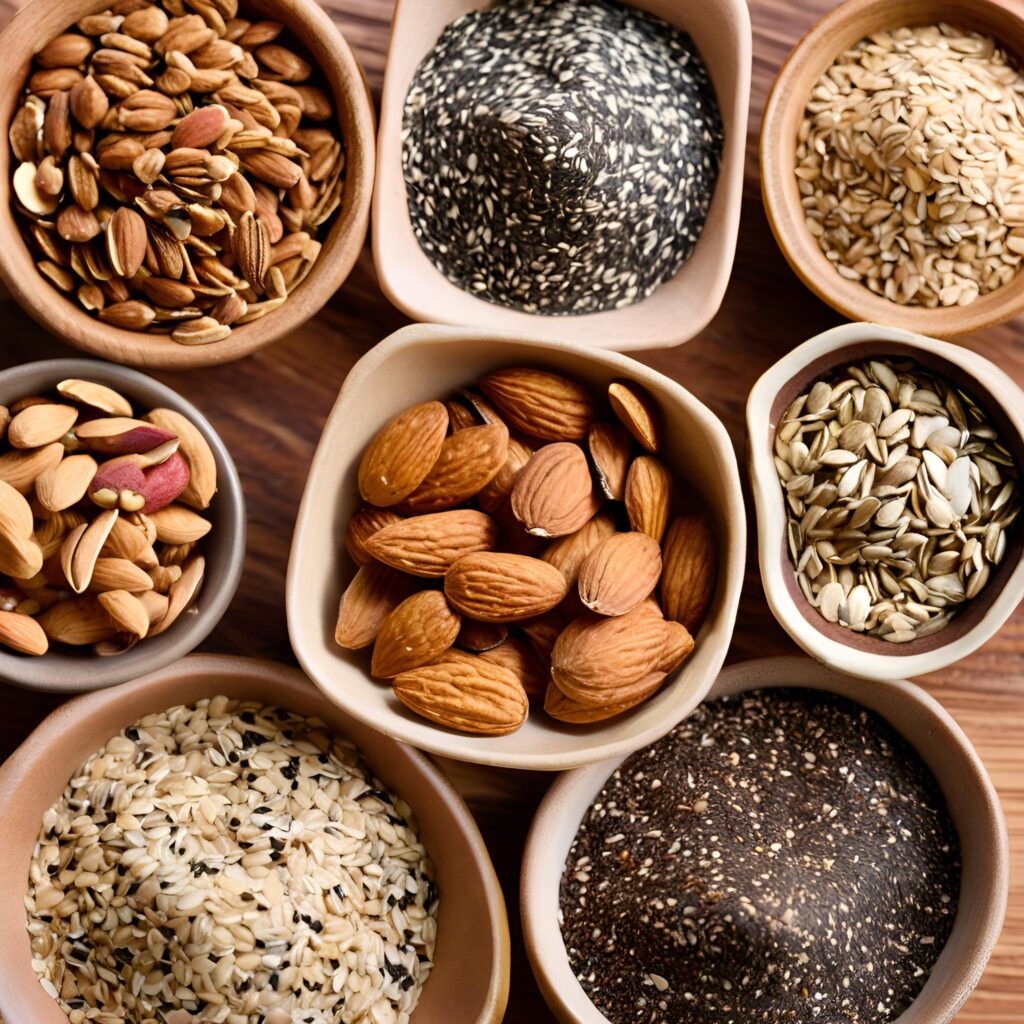



Iron-Rich Plant-Based Foods
- Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, Swiss chard
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, beans
- Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa
- Fortified foods: Plant-based milk, cereals
Calcium-Rich Plant-Based Foods
- Leafy greens: Kale, collard greens, broccoli
- Legumes: Tofu, tempeh
- Fortified foods: Plant-based milk, plant-based yogurt, fortified cereals
Vitamin B12 Sources
- Fortified foods: Plant-based milk, plant-based yogurt, fortified cereals
- Nutritional yeast
- Supplements
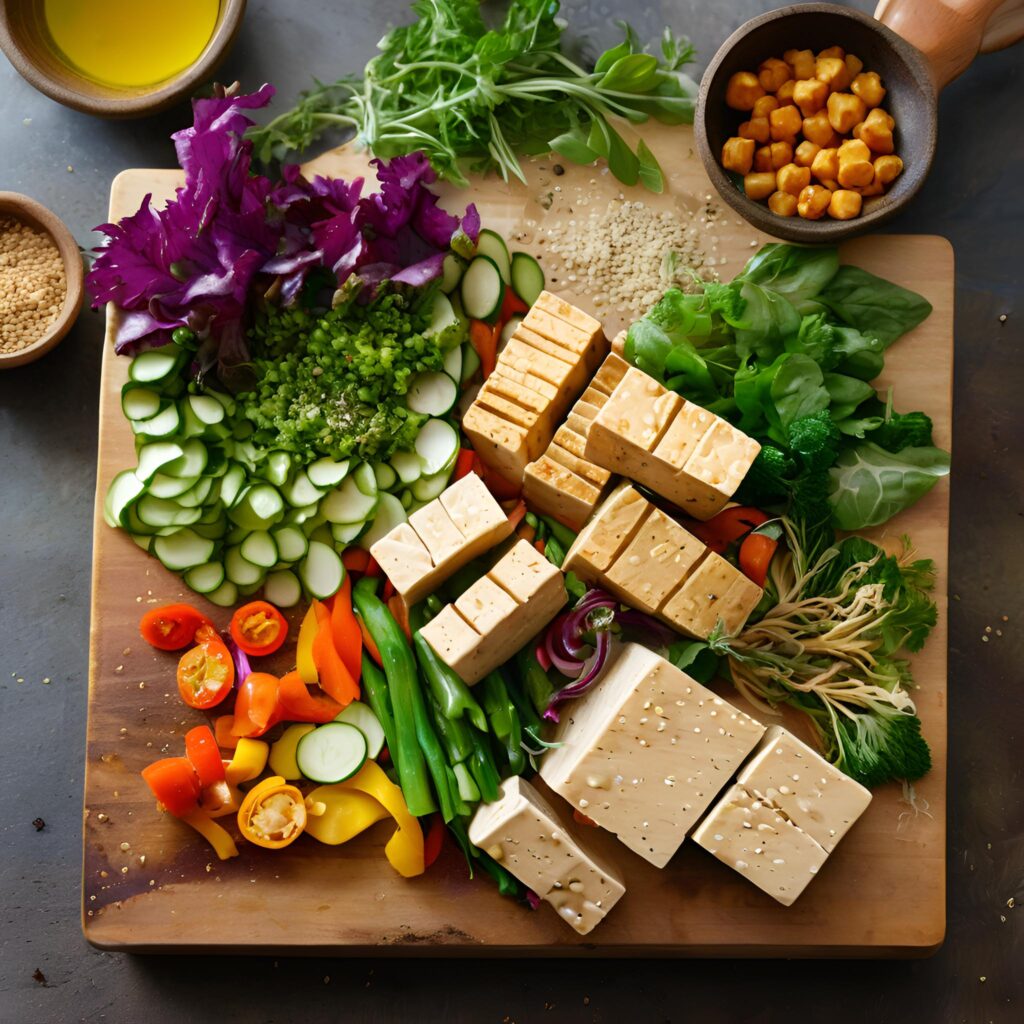
Meal Planning and Recipe Ideas
Meal planning can be a helpful way to stay on track with your plant-based diet. Here are some tips for meal planning:
- Stock your pantry with plant-based staples: This includes items like whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and spices.
- Plan your meals ahead of time: This will help you avoid making unhealthy choices when you're hungry.
- Find plant-based recipes you enjoy: There are many delicious plant-based recipes available online and in cookbooks.
Explore a wide range of plant-based products on Amazon (Paid link)
Here are a few simple plant-based recipe ideas:
- Lentil soup: A hearty and satisfying meal that's packed with protein and fiber.
- Vegetable stir-fry: A quick and easy meal that can be customized with your favorite vegetables.
- Whole grain salad: A refreshing and healthy salad that's perfect for lunch or dinner.
- Plant-based burgers: A delicious and satisfying alternative to meat-based burgers.
- Smoothies: A convenient and nutritious way to get your daily dose of fruits and vegetables.
Creating a Supportive Environment
Making the transition to a plant-based diet can be easier when you have support from friends and family. Here are some tips for creating a supportive environment:
- Educate your loved ones: Share information about the benefits of a plant-based diet and encourage them to try new plant-based foods.
- Join a plant-based community: Connecting with others who are following a plant-based diet can provide support and motivation.
- Find plant-based restaurants and grocery stores: This will make it easier to stick to your plant-based diet.
Final Thoughts on Following A Plant-based Diet
A plant-based diet can be a healthy and fulfilling way of eating, especially for older women. By following the tips in this guide, you can make a smooth transition to a plant-based lifestyle and enjoy the many benefits it has to offer. Remember, the most important thing is to find a plant-based diet that works for you and that you enjoy. With a little planning and creativity, you can easily incorporate more plant-based foods into your daily meals.



